The Middle East is a region spanning Southwest Asia and parts of North Africa. While the term ‘Middle East‘ is widely used, there is no universally accepted definition of the countries included within it.
This region stands as one of the world’s most strategically important regions, serving as a bridge between Asia, Africa, and Europe. It has been the cradle of human civilization and continues to shape global politics, economics, and cultural exchange.
For UPSC aspirants, understanding the Middle East is crucial as it significantly influences India’s foreign policy, energy security, and regional diplomacy.
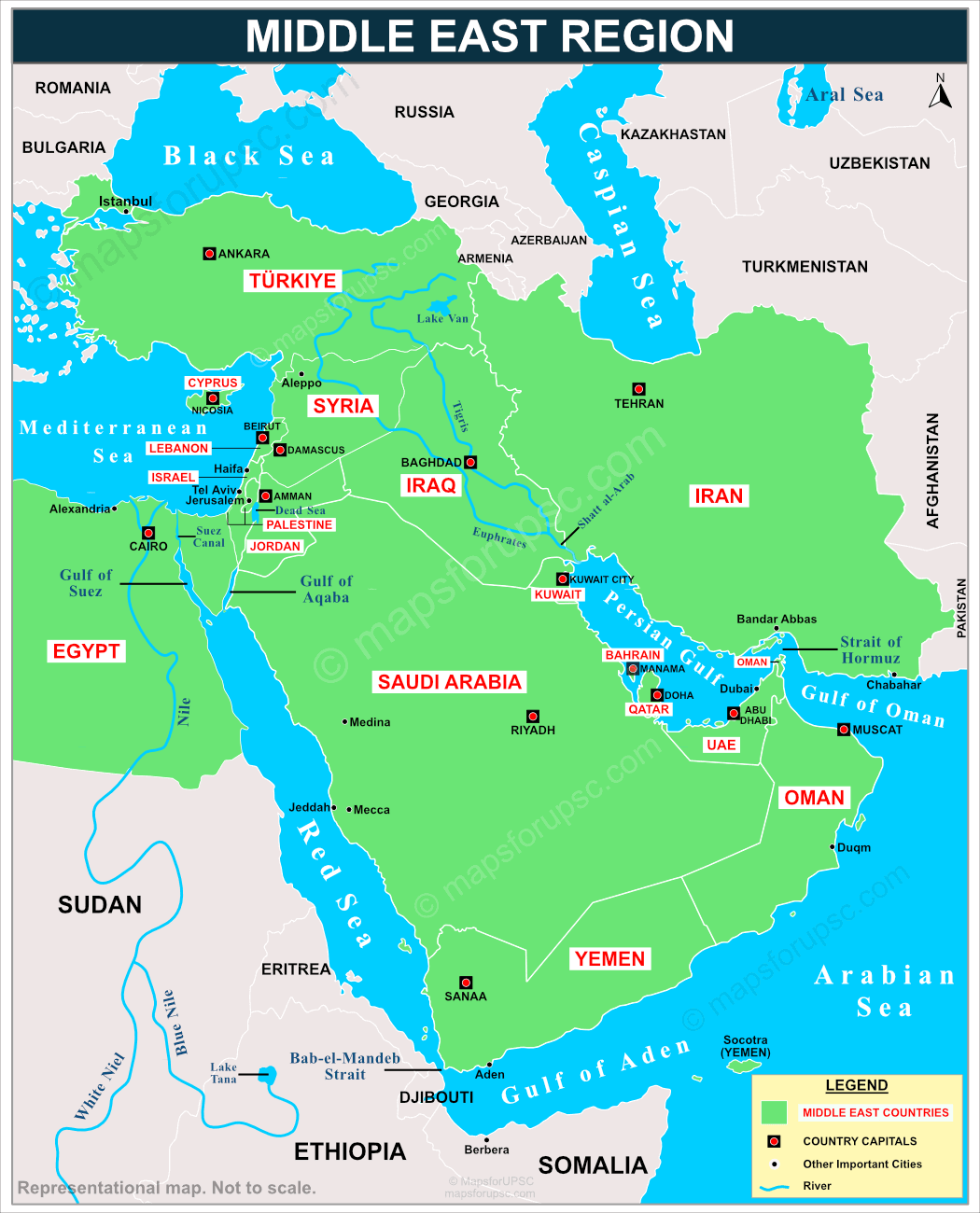

Middle East Countries List with Capitals
As noted earlier, the Middle East is not an officially defined grouping. Different organizations may include or exclude certain countries or territories, and some may not categorize it as a region at all.
However, the region shown in green on the map above represents a broadly accepted approximation of what is generally considered the Middle East.
The table below presents an alphabetical list of Middle Eastern countries, along with their capitals and currencies.
| S. No | Country | Capital | Currency |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bahrain | Manama | Bahraini dinar |
| 2. | Cyprus | Nicosia | Euro |
| 3. | Egypt | Cairo | Egyptian pound |
| 4. | Iran | Tehran | Iranian rial |
| 5. | Iraq | Baghdad | Iraqi dinar |
| 6. | Israel | Jerusalem** | Israeli shekel |
| 7. | Jordan | Amman | Jordanian dinar |
| 8. | Kuwait | Kuwait City | Kuwaiti dinar |
| 9. | Lebanon | Beirut | Lebanese pound |
| 10. | Oman | Muscat | Omani rial |
| 11. | Palestine | Ramallah** | Israeli shekel** |
| 12. | Qatar | Doha | Qatari riyal |
| 13. | Saudi Arabia | Riyadh | Saudi riyal |
| 14. | Syria | Damascus | Syrian pound |
| 15. | Turkey | Ankara | Turkish lira |
| 16. | United Arab Emirates | Abu Dhabi | UAE dirham |
| 17. | Yemen | Sanaa | Yemeni rial |
**Please Note:
- Jerusalem is claimed as the capital by both Israel and Palestine. Israel regards Jerusalem (including East Jerusalem, which it annexed in 1967) as its “eternal and undivided” capital. Palestine claims East Jerusalem as the capital of a future Palestinian state.
- Ramallah functions as the administrative seat of the Palestinian Authority, with many of its governmental offices located there. It is often treated as the de facto capital of the Palestinian territories due to restrictions on exercising authority in Jerusalem.
- The status of Jerusalem is unresolved under international law and diplomacy. Most countries (including India) do not officially recognize it as the capital of Israel (or of Palestine), preferring that final status over Jerusalem be determined through negotiations.
- India’s formal position: New Delhi does not recognize Jerusalem as Israel’s capital and is represented in Israel through its embassy in Tel Aviv. India supports a negotiated two-state solution and has consistently called for East Jerusalem to serve as the capital of a future Palestinian state, while expecting both Israel and Palestine to coexist peacefully.
- The Israeli shekel is the main currency in the Palestinian territories, though the Jordanian dinar and Egyptian pound are also used in some areas.
Key Facts and Strategic Importance
Economic Significance
Oil and Energy Resources: The Middle East contains a significant share of the world’s proven oil reserves, making it a key global energy hub. Major oil producers include:
| Rank | Country | Proven Reserves (Billion Barrels) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Saudi Arabia | 267 |
| 2. | Iran | 209 |
| 3. | Iraq | 145 |
| 4. | UAE | 113 |
| 5. | Kuwait | 102 |
Please Note:
Venezuela has the world’s largest proven oil reserves (~303 billion barrels), followed by Saudi Arabia, Iran, and Iraq.
Trade Routes: The region controls critical maritime chokepoints including the Suez Canal, Strait of Hormuz, and Bab-el-Mandeb Strait. The Suez Canal alone handles 12% of global trade and 30% of container traffic.
Cultural and Religious Significance
The Middle East is the birthplace of three major Abrahamic religions:
Islam: The dominant religion across the region, practiced by approximately 90% of the population in most Middle Eastern countries. The faith emerged in the Arabian Peninsula in the 7th century CE.
Christianity: Originated in the Levant in the 1st century CE, with significant communities still present across the region.
Judaism: The oldest of the three faiths, with its origins in the 6th century BCE, now primarily concentrated in Israel.
Strategic Waterways
Suez Canal: This 193-kilometer artificial waterway connects the Red Sea to the Mediterranean, reducing the sea route from Asia to Europe by up to 7,000 kilometers. It generates approximately $7 billion annually for Egypt.
Strait of Hormuz: A critical chokepoint through which significant portions of global oil exports pass, making it vital for global energy security.
Red Sea Route: Facilitates about 15% of global seaborne trade, including 8% of grain trade, 12% of oil, and 8% of liquefied natural gas.
Major Conflicts and Current Issues
Israel-Palestine Conflict
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict represents one of the world’s longest-running disputes, originating from competing national movements and territorial claims.

The status of Jerusalem has been described as “one of the most intractable issues in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict” due to the long-running territorial dispute between Israel and the Palestinians, both of which claim it as their capital city.
Most countries and organizations support that West Jerusalem and East Jerusalem should be allocated as capital cities to the Israelis and the Palestinians, respectively; this position has been endorsed by the United Nations, the European Union, and France, among others. Russia already recognizes East Jerusalem as the Palestinian capital and West Jerusalem as the Israeli capital.
Other key issues include:
- Territorial Disputes: Control over the West Bank, Gaza Strip, and East Jerusalem.
- Settlement Expansion: Israeli settlements in occupied territories remain a major source of tension.
- Recent Escalation: The October 7, 2023 Hamas attack triggered renewed conflict, leading to extensive military operations in Gaza.
Iran-Israel Tensions
The relationship between Iran and Israel has deteriorated into direct confrontation:
- Nuclear Program: Iran’s nuclear development remains a central concern for Israel and international community.
- Proxy Conflicts: Iran supports various groups including Hamas, Hezbollah, and Houthis against Israeli interests.
- 2025 Conflict: The “Twelve-Day War” in June 2025 marked a significant escalation in direct hostilities.
Regional Instability
Syrian Crisis: The ongoing civil war has created humanitarian disasters and regional spillover effects. The fall of Assad‘s regime in December 2024 has created new uncertainties.
Yemen Conflict: The Houthi-led insurgency has disrupted Red Sea shipping and created one of the world’s worst humanitarian crises.
Sectarian Tensions: The Sunni-Shia divide continues to fuel conflicts across the region, particularly between Saudi Arabia and Iran.
Importance for India
Energy Security
The Middle East supplies a significant portion of India’s crude oil imports, making regional stability crucial for India’s energy security. Disruptions in Middle Eastern oil production directly impact India’s economy through:
- Price Fluctuations: Conflicts cause oil price volatility, affecting India’s import bill.
- Supply Chain Disruption: Red Sea tensions force longer shipping routes via Cape of Good Hope.
Trade and Investment
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC): This ambitious infrastructure project aims to connect India to Europe via West Asia, potentially rivaling China’s Belt and Road Initiative.
Bilateral Trade: India maintains robust economic relationships with major Middle Eastern countries, including significant investments in energy and infrastructure.
Diaspora Connections
Over 8 million Indians work in the Gulf region, contributing significantly to India’s foreign exchange reserves through remittances. Their welfare remains a key consideration in India’s regional policy.
Strategic Partnerships
India maintains balanced relationships with competing regional powers:
- Israel: Defense cooperation and technology partnerships
- Iran: Energy cooperation and Chabahar Port development
- Arab Nations: Energy imports and investment opportunities
Area-Specific Important Facts
Golan Heights
- A plateau captured by Israel from Syria in the 1967 Six-Day War.
- Strategic for military control and water resources.
- Israel annexed it in 1981, but the move is not internationally recognized.
West Bank and Gaza Strip (Palestine issue)
- West Bank: under partial Palestinian Authority control, dotted with Israeli settlements.
- Gaza Strip: controlled by Hamas since 2007.
- Central to Israel–Palestine conflict, with repeated wars and humanitarian crises.
Strait of Hormuz
- Narrow waterway between Oman and Iran.
- About one-third of global seaborne oil passes through it.
- Vulnerable to blockades during tensions between Iran and the West.
Suez Canal (Egypt)
- Connects Mediterranean Sea with Red Sea.
- Key trade route between Europe and Asia.
- Blocked in 2021 by Ever Given, highlighting global dependence.
Bab el-Mandeb Strait (Yemen – Djibouti – Eritrea)
- Connects Red Sea to Gulf of Aden.
- Crucial for shipping to/from the Suez Canal.
- Security concerns due to Yemen conflict and piracy.
Kurdish regions (Iraq, Syria, Turkey, Iran)
- Kurds are the largest stateless ethnic group (~30–35 million).
- Demand for autonomy or independence has caused tensions in all four countries.
- Kurdish Peshmerga forces were key in fighting ISIS.
Shatt al-Arab River (Iraq–Iran)
- Formed by the confluence of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in Iraq.
- It serves as a strategic waterway and part of the Iraq–Iran border.
- Disputes over navigation rights and boundary demarcation were among the key triggers of the Iran–Iraq War (1980–88).
Hezbollah in Lebanon
- A Shiite militant and political group backed by Iran.
- Active along Israel’s northern border.
- Significant influence in Lebanese politics.
Northern Cyprus (Cyprus issue)
- Turkey occupies the northern third of Cyprus since 1974.
- Declared the “Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus,” recognized only by Turkey.
- Dispute involves Turkey, Greece, and the EU.
Houthi control in Yemen
- Houthis dominate northern Yemen including Sana’a.
- Engage in missile and drone attacks on Saudi Arabia and Red Sea shipping.
- Ongoing Saudi–Iran proxy rivalry.
